Laser Scanning Microscope Disadvantages

Light microscope transmission electron microscope scanning electron microscope and laser scanning confocal microscope.
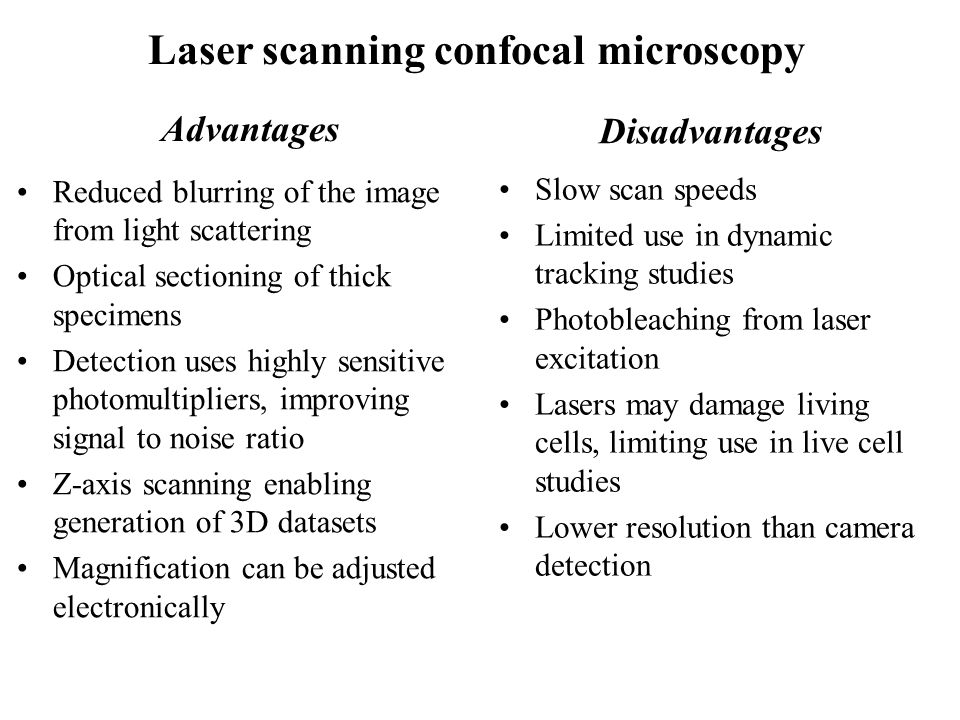
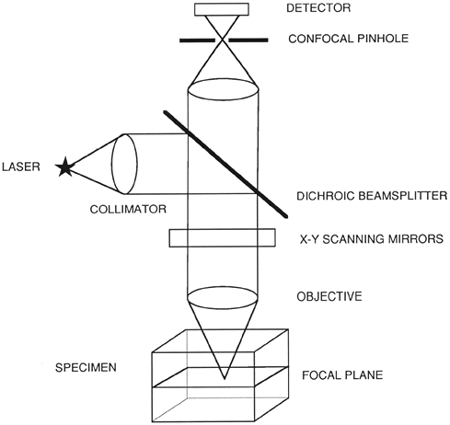
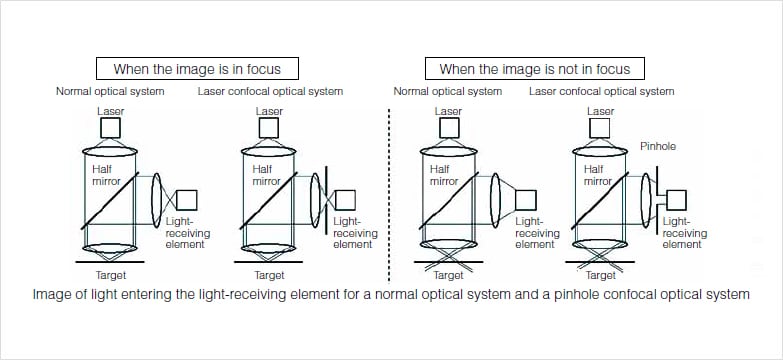
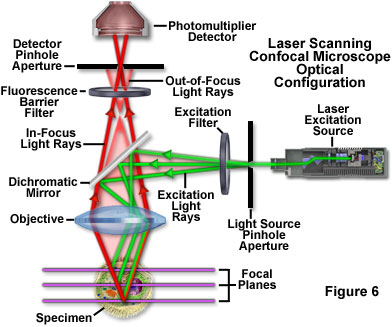
Laser scanning microscope disadvantages. When investigating multilayer structures the true surface of a substrate can be observed through a surface coating. In contrast conventional widefield microscopes use mercury or xenon based arc discharge lamps to provide a full range of excitation wavelengths in the ultraviolet visible and near infrared spectral regions. Laser scanning confocal fluorescence microscopy. A typical confocal uses raster scanning which means it scans the specimen point by point.
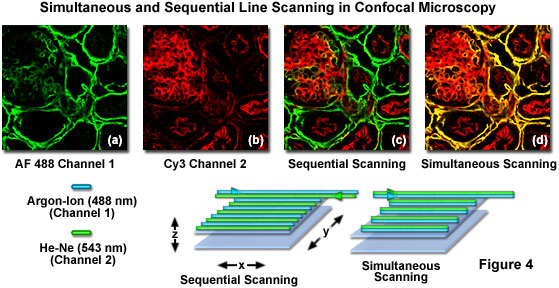
The laser scans across the object and an image is built up pixel by pixel on a screen. Electrons pass through the specimen and form an image. Imaging frame rates are typically slower for single point laser. A thick section of fluorescently stained human medulla in widefield fluorescence exhibits a large amount of glare from fluorescent structures above and below the focal plane figure 1 a.
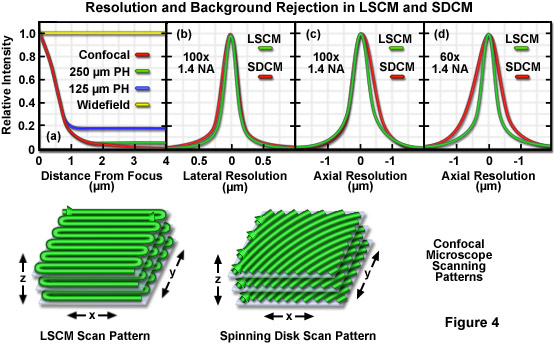
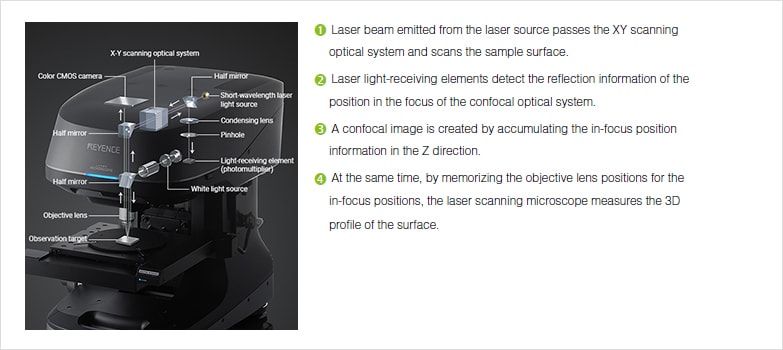
The confocal laser scanning microscope s aim was not to further increase magnification but to make clearer. Comparing to a wide field detection taking a snapshot of the whole field of view it is quite slow. The primary advantage of laser scanning confocal microscopy is to produce thin optical sections through fluorescent specimens that have a thickness beyond 50 micrometers. Confocal laser scanning microscopes can have a programmable sampling density and very high resolutions while nipkow and pam use a fixed sampling density defined by the camera s resolution.
Of course you can make it faster by compromising sensitivity resolution etc and there are some special implementation of confocal such as spinning disk confocal to resolve this issue. The thickness of the coating can be determined by observing the 2 peaks in the axial intensity variation. Laser scanning confocal microscopy. Advantages of confocal laser scanning microscopy industrial applications of confocal microscopy thin film profiling.
Electrons are reflected off the specimen to produce a 3d image. A the use of microscopy to observe and investigate different types of cell and cell structure in a range of eukaryotic organisms to include an appreciation of the images produced by a range of microscopes. Black and white images. When imaged with a laser scanning confocal microscope figure 1 d the.
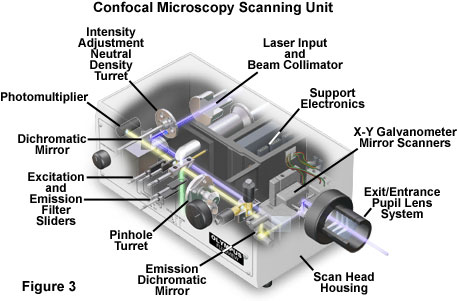
Spinning disk systems provide an alternative means of obtaining a full frame high speed confocal image in real time.











.jpg)